
RADIAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY
Experience Pain Relief with
Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
What is Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (R-ESWT)?
Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (R-ESWT) is a revolutionary, non-invasive treatment for chronic pain and soft tissue injuries. This non-invasive treatment uses pressure waves to reduce pain levels, trigger natural healing by stimulating circulation and cellular repair, break down scar tissue, speed up recovery, and provide fast, long-lasting relief—no surgery or medication needed. It’s especially effective for conditions like plantar fasciitis, tendon-related pain or dysfunction, and calcifications.
Whether you’re an athlete or just looking to live pain-free, Radial Shockwave Therapy can help you get back to what you love.
Discover the power of Radial Shockwave Therapy at
Las Vegas Physical Therapy and Sports today!

What Sets Us Apart?
At our clinic, you're not just getting standard care—you're getting treated by a team dedicated to evidence-based treatments. One of our practitioners, Dr. Robert Donatelli, has published articles on both Radial and Focused Shockwave Therapy, so you can trust that you’re in the hands of experts. This means you’ll be treated by professionals who have contributed to the body of research on this cutting-edge therapy.
Ibrahim, M. I., Donatelli, Robert. A., Hellman, M., Hussein, A. Z., Furia, J. P., & Schmitz, C. (2017). Long-term results of radial extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic plantar fasciopathy: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with two years follow-up. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 35(7), 1532–1538. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23403.
What Can You Expect?
Patients can typically expect several benefits from R-ESWT:
Pain Relief: R-SWT reduces pain by modulating pain signals and breaking down pain-related peptides.
Tissue Regeneration: Shockwaves stimulate collagen production and promote cellular proliferation, which helps repair injured tendons and other tissues.
Breaking Down Calcifications: One of the unique benefits of Radial Shockwave Therapy is its ability to break down calcium deposits in soft tissues, reducing stiffness and pain while improving mobility.
Neovascularization: Shockwave therapy encourages the formation of new blood vessels, which enhances blood flow to injured tissues, speeding up recovery.

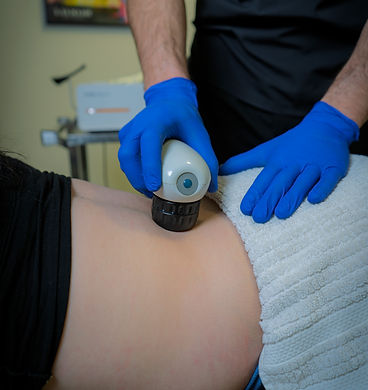
Why Choose R-ESWT?
Radial Shockwave Therapy has been successfully used for years to treat plantar fasciitis, tendinitis, and similar conditions. It’s especially effective for more superficial injuries and is a great alternative to surgery, offering quicker recovery times with minimal risks. Plus, when combined with Focused Shockwave Therapy, we can offer comprehensive care for more severe or deep-seated injuries.
Choose Your Path to Healing:
Transform Your Health with ESWT
01
Unlock Your Body's Healing Potential
04
Experience the ESWT Difference
02
Choose Advanced Healing with ESWT
05
Start Your Pain-Free Journey Today
03
Revolutionize Your Recovery Now
06

Get Started Today
Ready to relieve your pain? Schedule a consultation with our experienced team at Las Vegas Physical Therapy & Sports and see how Radial Shockwave Therapy can help you start living pain-free again!
Frequently Asked Questions
References:
-
Gerdesmeyer, L., Wagenpfeil, S., Haake, M., Maier, M., Loew, M., Wörtler, K., Lampe, R., Seil, R., Handle, G., Gassel, S., & Rompe, J. D. (2003). Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic calcifying tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA, 290(19), 2573–2580. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.19.2573
-
Ibrahim, M. I., Donatelli, R. A., Hellman, M., Hussein, A. Z., Furia, J. P., & Schmitz, C. (2017). Long-term results of radial extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic plantar fasciopathy: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with two years follow-up. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 35(7), 1532–1538. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23403
-
Wang C. J. (2012). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research, 7, 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-7-11
-
Gerdesmeyer, L., Frey, C., Vester, J., Maier, M., Weil, L., Jr, Weil, L., Sr, Russlies, M., Stienstra, J., Scurran, B., Fedder, K., Diehl, P., Lohrer, H., Henne, M., & Gollwitzer, H. (2008). Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is safe and effective in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant plantar fasciitis: results of a confirmatory randomized placebo-controlled multicenter study. The American journal of sports medicine, 36(11), 2100–2109. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546508324176
-
Burton I. (2021). Combined extracorporeal shockwave therapy and exercise for the treatment of tendinopathy: A narrative review. Sports medicine and health science, 4(1), 8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smhs.2021.11.002
-
Schroeder, A. N., Tenforde, A. S., & Jelsing, E. J. (2021). Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in the Management of Sports Medicine Injuries. Current sports medicine reports, 20(6), 298–305. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0000000000000851










.png)
.png)